When it comes to IT support, people often confuse a help desk with a service desk, assuming they serve the same purpose. While both are vital for resolving System errors and addressing user inquiries, their roles, scope, and approaches differ significantly. When it comes to IT support, the debate of “desk vs service” is common, many people confuse a help desk and service functions, thinking they are interchangeable.
This article unpacks the 6 critical differences between a help desk and a service desk to help you choose the right fit for your organization’s business needs. Understanding the differences between a help desk and a it service desk helps ensure that IT support meets both operational goals and the expectations of the end user. We’ll also explore how these desks handle incident management, Function request fulfillment, and align with Corporate aims. This article unpacks the help desk vs service comparison by exploring their differences in approach, scope, and alignment with business goals.
Stick around if you want to know:
- Which desk offers a more service-oriented and strategic focus.
- Why the it service desk often has a broader scope than a traditional help desk.
- How leveraging the right desk software ensures smoother support delivery and higher Client happiness.
Definition and Scope
A help desk and a service desk share the common goal of assisting users with Infrastructure faults. However, their primary focus and scope set them apart. A help desk and service desk both aim to provide technical support, but their methods and goals are distinct.
A help desk is often the first point of contact for resolving Immediate IT hurdles such as password resets, software glitches, or hardware malfunctions. Its task-oriented approach ensures quick resolutions to keep systems running smoothly. A help desk and a service desk share the common goal of assisting users with Technology problems. However, their key features and scope set them apart. Help desks are known for providing reactive support, tackling problems as they arise, and ensuring a timely response to minimize downtime. A help desk ensures that the end user can quickly resolve Critical system errors, minimizing disruption to their workflow.
On the other hand, a service desk has a broader scope that extends beyond fixing issues. It is designed to align IT support with an organization’s business goals. A service desk takes a proactive role by focusing on Incident handling, change management, and strategic IT planning. It serves as a bridge between IT and the business, ensuring the service lifecycle runs smoothly. By focusing on strategic planning and proactive IT management, a service desk aims to improve the overall experience of the end user, aligning IT services with broader business goals.
For example:
- A help desk might reset a user’s password when it’s forgotten.
- A service desk will not only reset the password but also assess whether better self-service portals or password policies can reduce such requests in the future.
By understanding their key differences, businesses can decide which model better meets their Strategic objectives and supports Long-term development.
6 Critical Differences Between Help Desk and a Service Desk
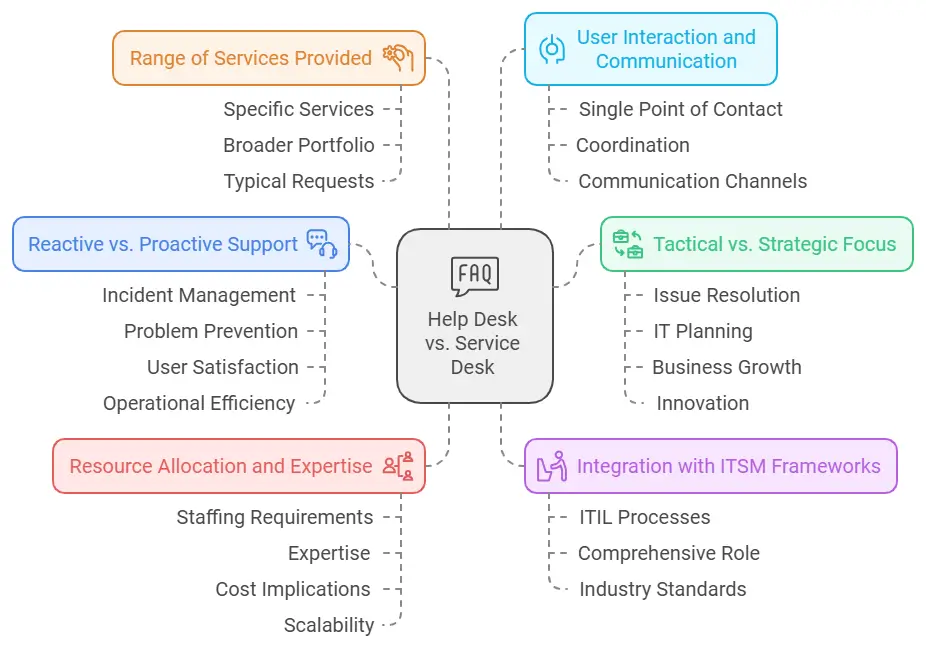
1. Reactive vs. Proactive Support
One of the most striking differences between a help desk and a service desk lies in their approach to technical support. The help desk vs service comparison starts with their approaches to Tech help
A help desk primarily provides reactive support, responding to Service requests and resolving Urgent IT problems as they arise. For instance, when a user encounters an error with software or hardware, the help desk is there to provide quick fixes. This approach ensures users can continue their work with minimal interruptions, maintaining operational efficiency in the short term.
In contrast, a service desk adopts a more proactive support model. It anticipates potential problems and takes steps to prevent them before they impact users. This proactive stance includes implementing Issue resolution strategies, analyzing incident trends, and ensuring effective knowledge sharing within IT teams. For example, a service desk tool might monitor system performance, identifying potential bottlenecks or security vulnerabilities before they disrupt operations.
Issue-focused help resolves immediate problems, allowing the end user to resume tasks. Proactive support prevents issues before they occur, enhancing productivity and satisfaction for the end user.
Why it matters:
- Reactive support addresses the symptoms of problems, while proactive support tackles the root causes.
- Organizations with a service desk often experience reduced downtime and improved User contentment, thanks to their forward-thinking approach.
By balancing the Issue-focused help of a help desk with the proactive strategies of a service desk, companies can deliver both immediate and long-term effective answers to users.
2. Tactical vs. Strategic Focus
A help desk has a tactical role in IT support. It is designed to handle routine tasks and assist users with System errors such as software troubleshooting, Client queries, and resolving immediate technical issues. The focus is on delivering solutions in a timely manner to ensure minimal disruption to daily operations. For example, help desk software can streamline ticket management to resolve user complaints faster.
A service desk, on the other hand, operates at a more strategic level. Its purpose extends beyond resolving day-to-day problems to aligning IT operations with the organization’s Strategic priorities. Service desks play a key role in:
- Change management to ensure smooth transitions during IT upgrades or migrations.
- Support delivery planning to meet agreed-upon performance standards, often outlined in a Service Level Agreement (SLA).
- Supporting end-to-end delivery of IT services in line with the organization’s business goals.
Example:
While a help desk resolves issues as they come, a service desk anticipates IT requirements for upcoming projects, ensuring resources and systems are prepared in advance. This strategic role enhances the organization’s ability to scale IT operations to meet Forward progress.
Why it matters:
Companies focused on long-term success need a support system that contributes to both immediate problem-solving and broader strategic alignment. By adopting a service Helpdesk system, businesses can enhance their aid delivery while maintaining operational excellence.
3. Integration with ITSM Frameworks
The roles of a help desk and a service desk differ significantly in their alignment with IT Service Management (ITSM) frameworks, such as ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library).
A help desk operates as a stand-alone function focused on handling user issues, providing quick solutions, and resolving technical problems. While it may loosely follow some ITIL practices, such as incident management, it rarely covers the broader Oversight workflows involved in ITSM.
Conversely, a service desk is deeply integrated into the principles of IT service management. It not only handles service requests and incidents but also supports Challenge mitigation, change management, and knowledge management. Its role is to ensure that IT services are delivered in a way that aligns with organizational Strategic objectives and goals.
Key examples of service desk alignment with ITSM frameworks include:
- Managing the service lifecycle from strategy and design to operations and continual improvement.
- Supporting sla management to ensure that agreed service levels are consistently met.
- Leveraging service desk tools to automate processes and improve efficiency.
Why it matters:
Organizations implementing ITSM frameworks benefit from the Larger domain of a service desk. It facilitates better coordination across IT teams, reduces human error, and ensures a seamless function delivery process.
By choosing a support desk approach, businesses gain a robust support system that promotes alignment between IT and overall Organizational goals, ensuring both immediate support and strategic IT planning.
4. Range of Services Provided
The services offered by a help desk and a service desk differ significantly in terms of breadth and complexity. While a help desk resolves individual queries, a service desk takes a holistic approach to IT assistance delivery, addressing the needs of both the business and the end user.
A help desk focuses on addressing technical issues and resolving Customer questions. Typical services include:
- Troubleshooting software and hardware problems.
- Resetting passwords and handling login issues.
- Providing support for minor technical issues and routine task-oriented activities.
Help desk software is tailored for quick problem resolution, ensuring minimal downtime and fast response times for users. It is best suited for organizations with straightforward IT needs, such as addressing immediate user concerns.
A service desk, on the other hand, provides a much wider array of services that encompass both IT support and strategic business alignment. In addition to handling incidents, it covers:
- Aid request fulfillment and tracking.
- Resource tracking to oversee IT hardware and software resources.
- Facilitating Data distribution through a centralized knowledge base.
- Supporting broader IT systems governance processes, including problem management and Transition management.
- Ensuring compliance with service level agreements (SLAs) to maintain high End-user approval.
Example of service desk capabilities:
While a help desk might resolve a single hardware issue, a service desk tracks the lifecycle of that asset, ensures it’s part of a replacement cycle, and integrates it into overall IT planning.
Why it matters:
Organizations with complex IT needs benefit more from the Expanded focus of services offered by a service platform. This allows IT teams to manage both end-user needs and organizational Company targets effectively, ensuring long-term solutions rather than short-term fixes.
5. User Interaction and Communication
The way a help desk and a service desk interact with users and stakeholders highlights another key difference. A help desk prioritizes resolving technical issues directly with the end user, whereas a service desk fosters collaboration between IT and other stakeholders to deliver solutions that benefit the end user more broadly.
A help desk typically acts as the single point of contact for addressing user issues. Its focus is on resolving tickets efficiently, ensuring minimal delays, and providing support for Regular responsibilities. This approach ensures that users receive direct assistance for their technical problems without unnecessary escalation. Most help desk software includes features like automated ticketing, FAQs, and self-service portals, which streamline user interactions.
A service desk, however, serves a dual purpose. It not only acts as the single point of contact for IT support but also facilitates communication between IT and other business units. This enables better alignment with Company demands and helps ensure that IT services contribute directly to achieving Operational aspirations.
How communication differs:
- A help desk prioritizes quick fixes for individual users, keeping interactions concise and task-specific.
- A service desk takes a more collaborative approach, involving IT teams, stakeholders, and service providers to deliver comprehensive solutions.
Example:
A help desk might respond to a user’s request for software installation. A service desk, on the other hand, will communicate with the IT team to ensure that the software aligns with licensing policies, resource availability, and organizational strategies.
Why it matters:
Effective communication is critical for achieving high Service satisfaction and maintaining operational efficiency. While a help desk ensures immediate support for users, a service desk approach fosters stronger collaboration between IT and the business, enabling more holistic solutions.
6. Resource Allocation and Expertise
The resource requirements and expertise involved in running a help desk versus a service desk vary greatly, reflecting their different scopes and responsibilities.
A help desk typically requires a smaller team with basic IT skills. These professionals focus on resolving Customer questions and addressing daily tasks, such as troubleshooting, password resets, and fixing hardware malfunctions. With the right help desk software, even a lean team can handle a high volume of support tickets efficiently. Both depend heavily on how teams manage their roles and responsibilities.
A service desk, in contrast, requires more extensive resources and a highly skilled workforce. The team often includes IT specialists experienced in problem management, Change oversight, and service level agreement monitoring. Additionally, service desk software plays a crucial role in managing the complexity of tasks, such as:
- Overseeing asset management to track and optimize IT resources.
- Facilitating knowledge management to empower teams with centralized information.
- Supporting strategic planning through integration with project management tools.
Cost and scalability considerations:
- A help desk is cost-effective for organizations with simpler IT support needs, making it ideal for smaller teams or SMEs.
- A service desk involves higher costs due to its advanced tools and Extensive reach but provides greater long-term value through its alignment with Operational ambitions and support for Scalability.
Why it matters:
Choosing between a Support desk software and a service Support desk software depends on the organization’s needs, budget, and IT complexity. Businesses focused on quick fixes and lower training costs might opt for a help desk, while those prioritizing scalability, strategic alignment, and Integrated delivery will find a service desk more suitable.
Implementation Considerations for SMEs
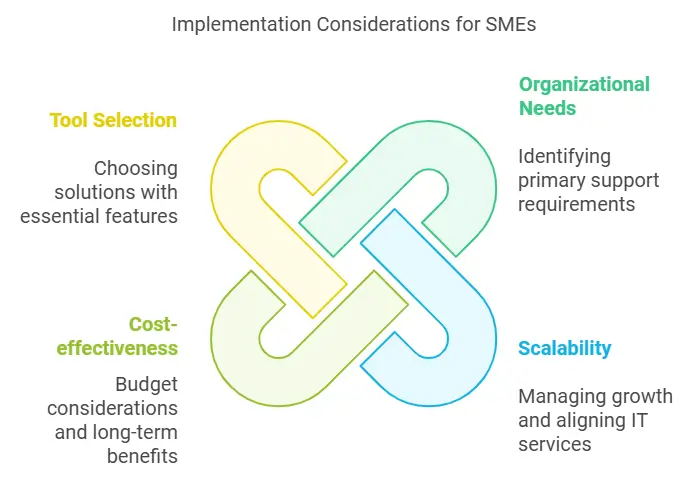
Small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often face unique challenges when choosing between a help desk and a service desk. Limited budgets, lean IT teams, and diverse business needs make it crucial to select a solution that aligns with the organization’s goals while optimizing operational efficiency.
Assess organizational needs:
Begin by identifying the primary support requirements. If the goal is to address immediate technical issues and resolve user inquiries efficiently, a help desk may suffice. However, if the organization requires strategic IT planning and support for complex processes like Change oversight and operations delivery, a service desk is the better option.
Evaluate scalability and future needs:
SMEs experiencing rapid growth should consider how their IT support will scale. A service desk tool offers capabilities for managing end-to-end delivery and aligning IT services with Strategic priorities, ensuring smooth transitions as the organization expands.
Cost-effectiveness:
Budget constraints are often a concern for SMEs. While help desk software is more affordable and simpler to implement, investing in a Service platform can yield better long-term benefits by reducing downtime, improving Consumer fulfillment, and supporting strategic IT initiatives.
Leverage the right tools:
Selecting the right desk software is essential. Look for solutions that offer features like ticket automation, Skill dissemination, and integration with existing systems. For SMEs, a tool that balances simplicity with robust functionality can bridge the gap between a help desk and a service desk.
Example for SMEs:
An SME with a lean IT team may start with a help desk solution to manage Customer concerns and streamline basic IT support. As the business grows, transitioning to a service desk approach enables the company to handle a wider range of IT operations, from asset management to proactive service request fulfillment.
Why it matters:
For SMEs, the decision between a help desk and a service desk has lasting implications for IT efficiency and alignment with business objectives. Starting with a clear understanding of current needs and future goals helps SMEs implement the most effective solution for their growth trajectory.
Best Practices and Recommendations
Implementing a help desk or a Assistance effectively requires more than just tools—it demands a thoughtful approach to processes, team training, and user experience. Whether your organization chooses a help desk solution or a service desk solution, following best practices can ensure success.
For Help Desks:
- Streamline ticketing systems: Use advanced help desk software to automate ticket assignments and track resolution times. This minimizes delays in handling user inquiries and improves Client happiness.
- Build a knowledge base: Empower users with self-service options by creating a repository of FAQs and troubleshooting guides. This reduces the volume of repetitive support requests.
- Focus on training: Train IT staff to handle diverse technical issues efficiently and ensure they are equipped to provide immediate solutions.
For Service Desks:
- Adopt ITSM frameworks: Align processes with industry standards like ITIL to ensure efficient service delivery and integration with broader Tech support process strategies.
- Monitor SLAs and KPIs: Regularly review performance metrics such as SLA commitment and resolution times to identify areas for improvement.
- Use the right tools: Invest in comprehensive service desk tools that support functions like Transition management, asset management, and knowledge sharing.
- Collaborate across teams: Foster communication between IT, business units, and service providers to align IT support with business objectives.
Additional Recommendations:
- Minimize downtime: Use proactive monitoring tools to detect potential issues before they disrupt operations.
- Enhance user engagement: Whether through a self-service portal or dedicated support team, prioritize creating a seamless user experience.
- Plan for scalability: As your business grows, ensure your IT support system evolves to meet increasing demands, from handling Daily operations to managing Lasting outcomes.
Why it matters:
By implementing these best practices, organizations can maximize the efficiency of their desk support systems, reduce human error, and achieve higher customer satisfaction. Whether you’re focused on solving immediate needs or planning for Scalability, following these recommendations helps your IT support align seamlessly with your Corporate aims.
Conclusion
Choosing between a help desk and a Operations boils down to understanding your organization’s specific needs, goals, and IT complexity. Both play vital roles in addressing user inquiries, resolving technical issues, and maintaining IT operations. However, their Core variations lie in their scope, focus, and integration with broader IT service Governance systems. When evaluating “help desk vs service”, the right choice depends on your organization’s IT requirements and growth plans.
A help desk is best suited for organizations looking to provide quick, Responsive assistance for day-to-day technical issues. It offers a cost-effective solution for managing Ongoing duties and ensures minimal downtime. Its robust capabilities in incident management, asset tracking, and SLA management provide a competitive edge.
A Operations, with its Wider range and Support-oriented approach, is ideal for businesses aiming to align IT with their business objectives. By adopting a service desk solution, organizations can manage complex processes such as System adaptation process, incident management, and asset management while supporting strategic growth.
Both options can lead to enhanced customer satisfaction and improved operational efficiency when implemented with the Proper resources and processes. Assess your business’s needs, plan for future growth, and leverage the appropriate desk software to achieve the best results.
FAQs
1. What is the primary difference between a help desk and a service desk?
The main difference is scope and focus. A help desk provides Responsive assistance for Technology problems and user inquiries, while a Support desk offers a broader range of services, including proactive IT planning, service request fulfillment, and alignment with Company targets.
2. Can a small business benefit from a Function desk?
Yes. While a help desk solution may initially meet the needs of small businesses, a Support desk solution can support future growth by aligning IT with strategic objectives, improving service delivery, and reducing downtime through proactive support.
3. Are help desks and service desks both part of ITSM frameworks?
A Function desk is an integral part of IT Service Management (ITSM) frameworks like ITIL, focusing on managing the entire Assistance lifecycle. A help desk often works as a standalone function, addressing basic support needs without full ITSM integration.
4. What kind of software is used for help desks and service desks?
Help desk software focuses on ticketing, FAQs, and self-service portals to handle user requests efficiently.
Service desk software supports advanced features such as asset management processes, knowledge management, change management, and SLA tracking.
5. How do service desks contribute to customer satisfaction?
Service desks enhance customer satisfaction by providing long-term solutions, ensuring smooth service delivery, and maintaining high levels of performance through strict Support performance pact.