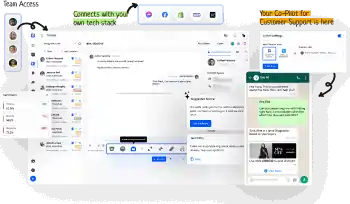
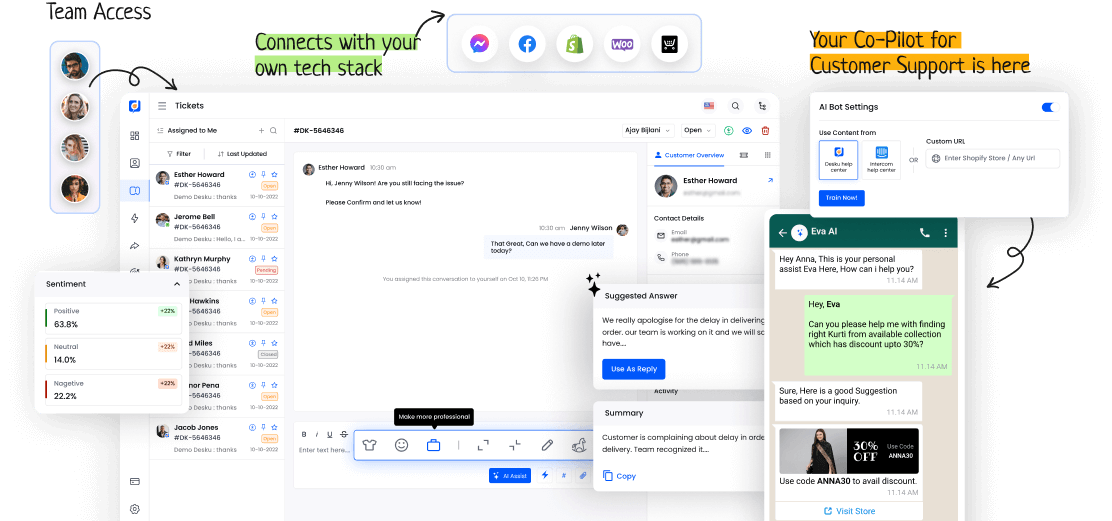
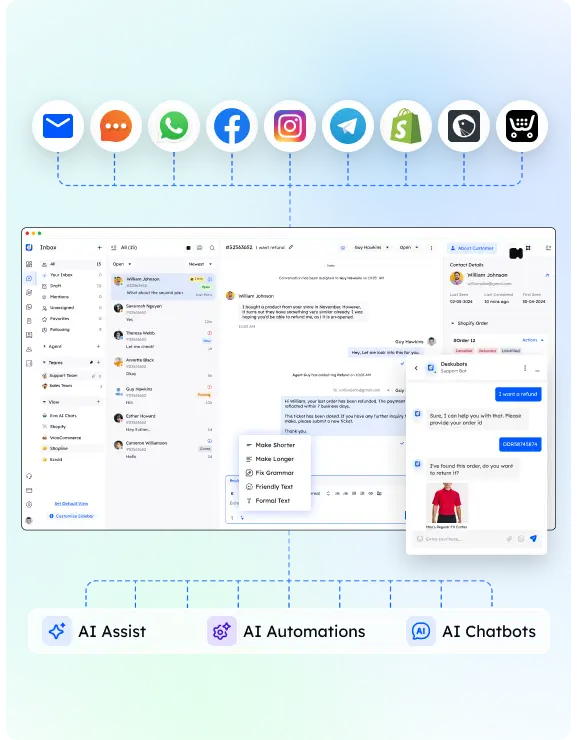
In tech support systems, the Agent Interface is key. It helps smooth user interactions and problem solving. It's not just for talking. It's a pathway for users to handle complex issues and get help quickly.
But, to grasp this interface, you have to look beyond its basic uses. You must step into a world where user experience meets top-notch service. Let's explore what an Agent Interface really is and how it changes customer support in the digital world.
I. Definition of Agent Interface
The Agent Interface is vital in tech support systems. It's the main connection point between users and the software or service.
It's a communication tool that lets users interact with the system, get help, and get support.
This interface is crucial for good user interaction and smooth communication between users and the system.
II. Importance and Functionality of Agent Interface
The Agent Interface plays a key role in tech support systems. It boosts communication and engages with users. It makes interactions easier, gives help instantly, and improves customer happiness.
It has critical functions like chatting, knowledge base access, and ticket handling. These features make a smooth and effective platform for agents to help users quickly and efficiently.
III. Applications and Examples of Agent Interface
Agent Interface finds use in many industries, showing its adaptability and success in bettering customer support encounters.
- Virtual helpers make interactions smooth.
- Customer support sees faster response times.
- Automated methods boost effectiveness.
- Tailored experiences result in happier customers.