Choosing the right ecommerce revenue model is essential for shaping your business strategy, driving predictable income, and supporting long-term growth. Whether you’re launching a new venture or refining an existing one, understanding different revenue models—like the interest revenue model—can help align your strategy with customer needs.
This guide explores seven top ecommerce revenue models, complete with examples and tips to help entrepreneurs, marketers, and ecommerce platform builders find the best fit for their goals.
Understanding Ecommerce Revenue Models
An Internet sales strategy is the blueprint for how your business generates revenue. For businesses exploring unique avenues like interest revenue model, It defines the way companies sell physical goods, services, or software products to their customers. The right revenue model ensures predictable income, aligns with consumer preferences, and supports long-term business growth.
Different b2b revenue models work for different business models. A subscription model, for instance, is particularly common for companies offering recurring services or content. A transaction fee-based model is ideal for platforms where the intermediary charges commission fees to sellers or buyers for facilitating transactions. An Online income framework forms the backbone of your overall business model, dictating how you generate income and engage with customers.
When choosing or modifying a revenue strategy, businesses should consider factors such as their Intended market, customer segments, and Core offering. For example, B2B revenue streams often rely on strategic partnerships and recurring fees, while B2C models may focus on direct sales or pay-per-use pricing strategies. When a company resells data, it transforms anonymized customer insights into valuable resources for marketers, advertisers, or research institutions.
It’s also essential to consider your company’s resources and market positioning. Some company’s revenue streams, like advertising campaigns or Metrics analysis, require advanced tools and expertise. Others, like equipment-as-a-service or a usage-based model, rely on offering unique customer value, such as lower upfront costs or flexible pricing.
Here are some critical aspects to keep in mind when evaluating ecommerce revenue models:
- Customer Behavior: Does your Customer base prefer to customers pay small amounts over time, or are they comfortable with higher upfront costs?
- Revenue Diversification: Can you add Alternative profit pathways like Advertising slots, professional services, or intellectual property licensing?
- Scalability: Will this model grow with your business? Subscription models, for example, are ideal for scaling, as recurring payments from existing customers generate steady income.
- Market Trends: How do new revenue streams align with customer demands and industry trends, such as the rise of financial institutions offering software equipment-as-a-service?
By understanding these factors, businesses can not only select the most common revenue model for their type of operations but also identify opportunities for creating innovative Profit avenues. Among these, the subscription model is a particularly common model for businesses offering recurring services, such as software solutions or media platforms. With Business intelligence and a clear business strategy, companies can refine their approach to maximize Income earned.
The 7 Best Ecommerce Revenue Models
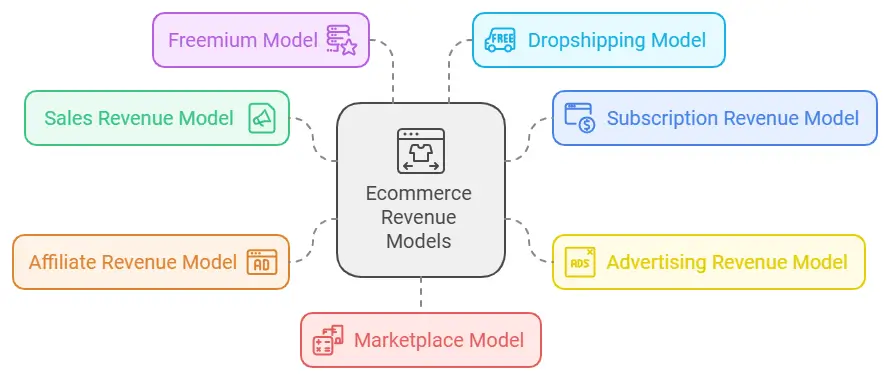
Ecommerce businesses have a variety of revenue models to choose from, each catering to different customer needs and business goals. Below are the seven most common revenue models, along with their benefits, examples, and tips to help you decide which one might work best for your business.
1. Sales Revenue Model
This is the classic revenue model, where businesses generate revenue by selling physical or software products directly to customers. It’s one of the most common b2b revenue models in ecommerce and is straightforward to implement.
- How it Works: Customers pay small amounts for products at a collects fixed fees difference, either online or in-store.
- Examples: Companies like Amazon, Shopify stores, or businesses selling digital downloads.
- Pros: Simple to understand, offers full control over Costing approach, and scales easily with inventory.
- Challenges: Requires significant effort in inventory management, Pricing plan, and customer acquisition.
- Pros: Simple setup, ideal for businesses selling physical or software product. Offers flexibility in pricing and revenue generation.
- Cons: Requires inventory management, higher upfront costs, and marketing efforts to attract new customers.
2. Subscription Revenue Model
A Recurring revenue scheme allows businesses to collect recurring fees in exchange for ongoing access to products or services. It’s a particularly common model for software solutions, streaming platforms, and membership-based ecommerce businesses.
- How it Works: Customers pay a recurring fee—monthly, quarterly, or annually—to maintain access.
- Examples: Netflix, Spotify, or Dollar Shave Club.
- Pros: Predictable income, strong User retention, and opportunities for upselling.
- Challenges: Requires consistent value delivery to keep subscribers engaged.
- Pros: Ensures recurring revenue and predictable income. Builds strong customer loyalty and retention.
- Cons: Demands consistent delivery of value and high-quality customer service to maintain subscriptions.
3. Affiliate Revenue Model
With the affiliate model, businesses generate classic revenue model by earning a commission for promoting and selling products or services from other businesses. It’s an excellent Financial model for blogs, influencers, and digital marketers.
- How it Works: You share affiliate links, and when customers pay through those links, you earn a percentage of the revenue.
- Examples: Affiliate programs run by Amazon, ClickBank, and Shopify.
- Pros: No need to manage inventory or shipping.
- Challenges: Success depends on the ability to drive traffic and conversions.
- Pros: Low operational costs and no inventory management . Scales well with traffic growth.
- Cons: Earnings depend on the volume and conversion rates of referred customers. Requires effective marketing strategies.
4. Advertising Revenue Model
The Promotional framework involves selling ad space on your ecommerce platform, website, or app. It’s particularly common for businesses with significant traffic or niche audiences.
- How it Works: Revenue is generated by displaying ads, charging on a cost-per-click (CPC), cost-per-thousand impressions (CPM), or pay-per-action basis.
- Examples: Google, Facebook, or websites monetizing through ad networks.
- Pros: Generates Secondary income streams without needing to sell products.
- Challenges: Requires high traffic and strong Analytical tools to attract advertisers.
- Pros: Generates Extra income channels without selling products. Works well for platforms with high traffic or niche audiences.
- Cons: Requires data analysis tools, consistent audience engagement, and trust from advertisers.
5. Freemium Model
The freemium model gives customers free access to basic services or products while offering premium features for a cost. This model works well for software solution and intellectual property-based businesses.
- How it Works: Customers can use a free version but pay for advanced features or additional benefits.
- Examples: LinkedIn Premium, Canva, or Zoom.
- Pros: Attracts a wide user base quickly.
- Challenges: Balancing free and paid features to encourage conversions without deterring users.
- Pros: Attracts a large audience quickly with free offerings. Provides opportunities to upsell premium features.
- Cons: Balancing free and paid features can be challenging. Risk of users relying on free services without upgrading.
6. Dropshipping Model
The dropshipping model allows businesses to sell products without holding inventory. Instead, third-party suppliers handle inventory, shipping, and fulfillment.
- How it Works: The business acts as an intermediary, charging customers and then forwarding orders to suppliers.
- Examples: Oberlo-powered Shopify stores.
- Pros: Low startup costs and risk.
- Challenges: Thin margins and potential delays due to reliance on third-party suppliers.
- Pros: Eliminates the need for inventory and reduces upfront costs. Flexible and easy to start.
- Cons: Margins are slim, and you’re reliant on suppliers for timely delivery and product quality.
7. Marketplace Revenue Model
In the marketplace model, the intermediary charges commission fees for each transaction facilitated between buyers and sellers, often supplementing income with advertising or subscription services.
- How it Works: A company facilitates transactions, collects fixed fees or percentage commissions, and may generate additional revenue through ads or premium memberships.
- Examples: eBay, Etsy, and Airbnb.
- Pros: Scalability and multiple Earnings channels from advertising, premium services, and transaction fees.
- Challenges: Requires robust technology, user trust, and a large audience base to thrive.
- Pros: Generates revenue from multiple streams, including transaction fees and ad space. Scalability is high as the marketplace grows.
- Cons: Requires substantial investment in technology, marketing, and building trust between buyers and sellers.
Each of these b2b revenue models aligns with specific business needs, customer segments, and Target customers. Choosing the right revenue model can depend on your value proposition, marketing strategies, and ability to meet customer demands.
Key Considerations When Comparing Revenue Models
- Primary audience: Businesses with large audiences may benefit more from advertising models, while niche markets might excel with subscription or affiliate models.
- Business Strategy: Direct sales suit companies selling physical goods, while B2B revenue models like subscriptions or licensing work better for software or service-based businesses.
- Scalability: Models like subscription and freemium offer predictable growth, while dropshipping and marketplaces need constant optimization to scale. When designing your business model, scalability and customer alignment should guide your choice of Financial streams.
- Revenue Diversification: Adding additional Income sources, like ad space or affiliate marketing, can boost income without overhauling your business model.
By analyzing these factors, ecommerce businesses can choose a model—or combination of models—that fits their needs and helps generate revenue effectively. A particularly common model like the sales or subscription approach can cater to broad audiences, but businesses should same asset whether it aligns with their specific value propositions and market dynamics.
Implementing the Right Revenue Model
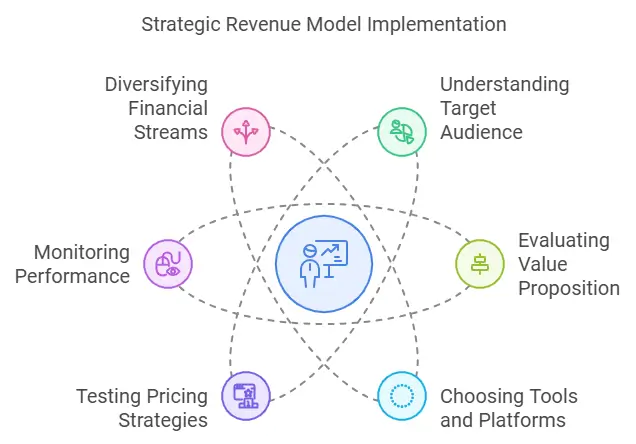
Selecting the Best-fit revenue structure is only half the journey. Successful implementation requires a combination of strategy, tools, and adaptability to ensure it aligns with your business goals and customer expectations. Here’s how to put your chosen most common revenue model into action effectively.
1. Understand Your Target Audience
Every different revenue models hinges on meeting customer needs. Conduct data analysis to identify your Focus group, customer segments, and preferences. For example:
- Subscription Models: Best suited for customers who value ongoing service or convenience.
- Sales Models: Ideal for audiences looking for physical goods or one-time purchases.
Use tools like surveys, social media insights, and analytics platforms to get a clear picture of your target market.
2. Evaluate Your Value Proposition
Your value proposition should align with your chosen revenue model. For instance:
- If you’re adopting an affiliate revenue model, ensure you’re promoting products or services that resonate with your audience.
- With a freemium model, provide enough value in the free version to attract users, while reserving premium features that justify a recurring fee.
Clearly communicate how your business generates revenue while delivering value to customers.
3. Choose the Right Tools and Platforms
The success of your revenue model depends on using the right tools.
- For Subscription Models: Use platforms like ReCharge or Bold Commerce to manage recurring fees and billing.
- For Advertising Models: Tools like Google Ad Manager can help optimize Marketing inventory and campaigns.
- For Dropshipping: Services like Oberlo simplify inventory and supplier management.
Ensure your platform integrates well with payment gateways, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and Business intelligence tools to track revenue generated.
4. Test Pricing Strategies
Your pricing strategy can make or break your revenue stream. Experiment with options like:
- Tiered Pricing: Offer basic, premium, and enterprise packages.
- Pay-per-Use: Charge customers usage-based-model, particularly effective for businesses offering professional services or software solution.
- Discounts and Incentives: Test limited-time offers to attract customers and build initial traction.
Monitor customer responses and modify your pricing if necessary to balance value and profitability.
5. Monitor and Optimize Performance
Consistent monitoring is critical to refining your Income plan. Key steps include:
- Track Metrics: Measure Client loyalty, conversion rates, and revenue growth.
- Collect Feedback: Use reviews, surveys, and support interactions to understand customer pain points.
- Adapt Quickly: Be ready to adjust to market trends, like introducing new Income sources or modifying existing ones.
For example, if you notice a drop in recurring subscriptions, it may be time to rethink your content delivery or customer engagement tactics.
6. Consider Diversifying Financial streams
Even with a primary revenue model in place, adding secondary Profit avenues can enhance stability and growth. For instance:
- Ad Space: Monetize your platform traffic.
- Data Licensing: If your company resells data, ensure it’s anonymized and complies with regulations.
- Affiliate Partnerships: Collaborate with other businesses to expand your offerings and generate additional income.
By focusing on these steps, ecommerce businesses can not only implement the Effective earnings plan but also adapt and grow with changing market conditions. Success lies in striking a balance between meeting customer needs and realized savings your revenue potential.
Case Studies: Ecommerce Revenue Models in Action
Real-world examples are an excellent way to see how businesses pay successfully use different b2b revenue models. Similarly, lending money platforms could leverage marketplace models to connect borrowers and lenders, earning revenue through transaction fees or subscription tiers. Beyond transaction fees, the company earns interest on escrowed funds held temporarily during bookings. Below are case studies showcasing how companies leverage their revenue strategies to grow and thrive.
1. Amazon – Sales Revenue Model
Amazon’s primary revenue stream comes from the sales revenue model examples, where the company generates income by selling a vast array of physical goods. However, Amazon has diversified its additional revenue streams to include subscription services like Prime and Marketing efforts.
- How They Excel: Amazon’s Pricing framework, combined with its robust logistics network, ensures higher price difference and fast delivery. This keeps customers coming back.
- Takeaway: Focus on delivering convenience and building trust to retain customers.
2. Netflix – Subscription Revenue Model
Netflix exemplifies the Membership plan, generating revenue through monthly recurring fees. The platform uses customer data analytics to predict income and improve its content recommendations, enhancing user retention.
- How They Excel: Netflix continually reinvests in original content, ensuring a value proposition that competitors struggle to match.
- Takeaway: Regularly add value to justify recurring fees and keep subscribers engaged.
3. Shopify – Freemium and Subscription Models
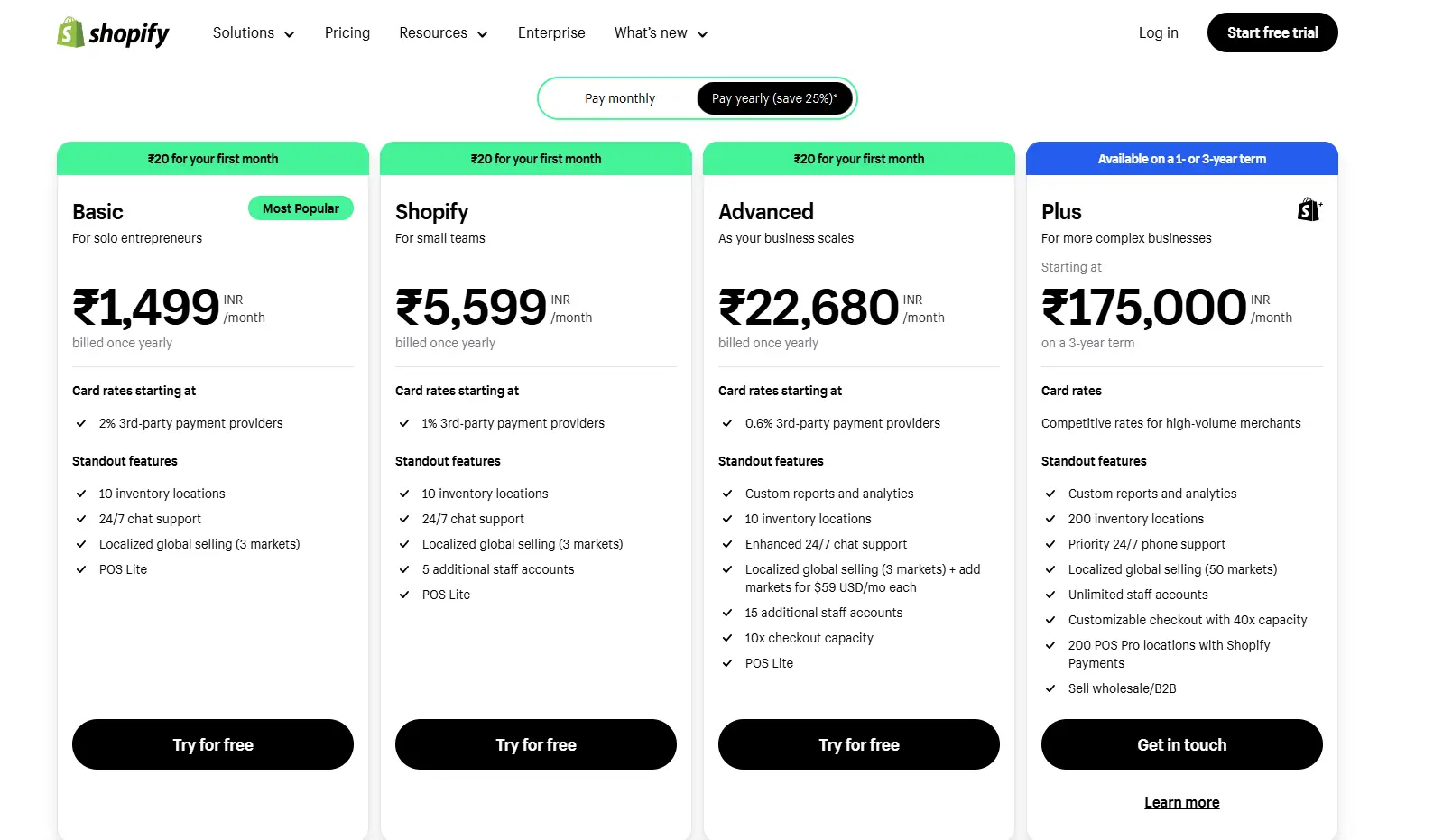
Shopify combines a freemium model with subscription Profit avenues. Small businesses can start with a free trial, while premium features and integrations come at a recurring cost.
- How They Excel: By offering scalable plans, Shopify accommodates businesses of all sizes.
- Takeaway: Use tiered price difference to appeal to a broader target customers and upsell as businesses grow.
4. Airbnb – Marketplace Revenue Model
Airbnb operates on a marketplace Financial structure, where it charges intermediary commission fees to both hosts and guests. The platform also earns revenue from additional services like travel experiences.
- How They Excel: Airbnb builds trust through user reviews and seamless transactions, enabling them to charge premium fees.
- Takeaway: Foster trust and user satisfaction in marketplaces to increase your earning potential.
5. Oberlo – Dropshipping Model
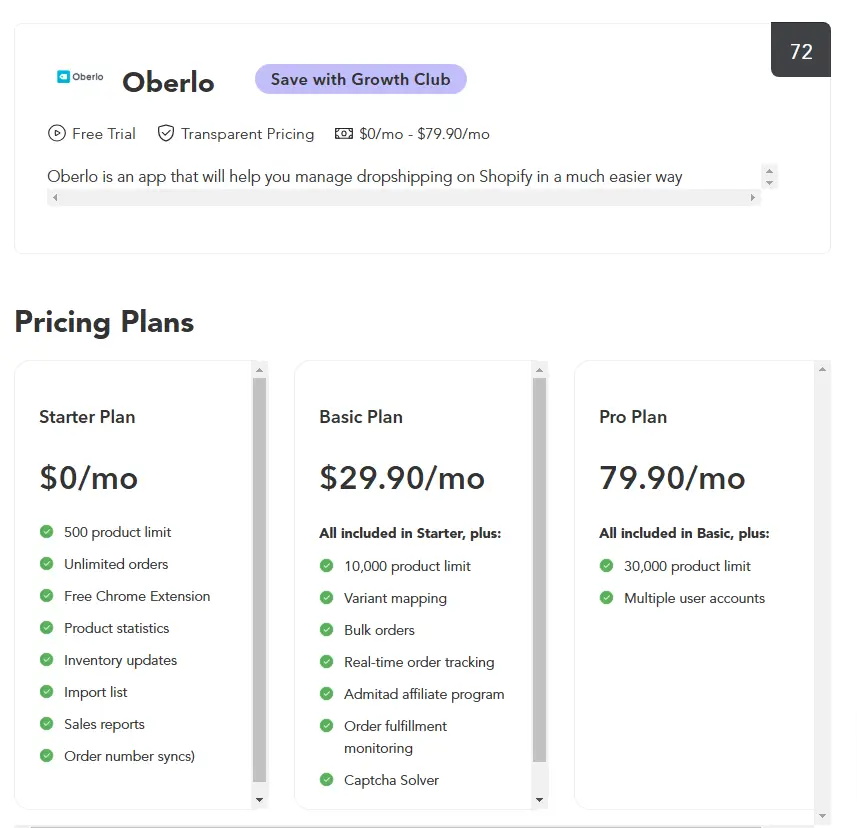
Oberlo, a Shopify app, company facilitates the dropshipping model, where users can start ecommerce stores without holding inventory. The platform Creates income by offering subscription plans to access its features.
- How They Excel: Oberlo simplifies the supply chain, allowing entrepreneurs to focus on marketing and customer service.
- Takeaway: Use a unique value proposition like inventory-free selling to attract budding entrepreneurs.
6. Google – Advertising Revenue Model
Google’s advertising model is a powerhouse, generating revenue by selling Banner space across its platforms, including search results, YouTube, and Google Cloud Platform.
- How They Excel: Advanced data analytics and personalized ad targeting make Google’s ads highly effective, driving demand from advertisers.
- Takeaway: Invest in data-driven insights to optimize your advertising Revenue pathways.
These examples highlight the flexibility of ecommerce revenue models and the importance of tailoring them to your Corporate plan. By learning from these successes, you can adapt similar techniques to boost your own revenue.
FAQs
1. What is the most common ecommerce revenue model?
The sales revenue model is the most common, where businesses Drive profits by selling physical or software product directly to customers. It’s simple to implement and works well for a wide range of businesses.
2. How can I choose the Ideal monetization strategy for my ecommerce business?
Start by understanding your Intended market, evaluating your value proposition, and same asset your Business roadmap. Consider factors like user preferences, scalability, and the resources needed to implement each model.
3. Can I combine multiple revenue models in my business?
Yes! Many businesses use a combination of models to diversify their Earnings channels. For instance, Amazon uses sales, subscription, and advertising models to generate revenue from different consumer segments.
4. What tools can help me implement my chosen revenue model?
The tools you use depend on your model:
Subscription models: Platforms like ReCharge and Bold Commerce.
Advertising models: Tools such as Google Ad Manager.
Dropshipping models: Apps like Oberlo for supplier management.
5. How do I transition to a new revenue model?
Evaluate your current Financial streams and identify opportunities for improvement. Start small by testing the new model with a specific product or audience segment, then scale gradually based on performance and feedback.
6. How does choosing a revenue model affect how a business manages money?
The Optimal revenue framework provides clarity on income streams, allowing businesses to better manages money for investments, operations, and customer acquisition strategies.
Conclusion
Selecting the right ecommerce revenue model is key to driving growth and meeting customer needs. From One-to-one selling to subscription and marketplace models, each offers unique benefits. Whether you adopt In-person selling, subscriptions, or marketplace models, each offers opportunities to align with your target audience and unlock realized savings. By diversifying revenue models, businesses can include innovative methods where a company earns interest alongside traditional income streams like sales and subscriptions. Success depends on aligning your model with your target audience, monitoring performance, and staying adaptable to trends.
Whether your business focuses on selling physical products, offering subscription-based services, or even lending money, selecting the right ecommerce revenue model ensures scalability and long-term success. Focus on creating value, diversifying Profit avenues, and refining your strategy to build a sustainable, thriving ecommerce business.