When it comes to managing customer interactions, the terms “customer support” and “customer service” are often used interchangeably. But are they the same? Not exactly. While both play crucial roles in ensuring customer satisfaction, they focus on different aspects of the customer journey.
Customer support focuses on resolving technical problems and assisting with product-related issues. On the other hand, customer service encompasses broader activities aimed at building strong customer relationships and fostering loyalty.
In this article, we’ll break down the key differences between customer support and customer service, explore their unique roles in business success, and highlight why combining both functions leads to exceptional customer experiences.
By the end, you’ll understand how to align your customer support teams and customer service representatives to create a seamless experience that enhances satisfaction, boosts retention, and drives business growth.
Defining Customer Support
Customer support focuses on addressing technical issues and assisting customers with product-related problems. This function is critical for ensuring a positive experience with a company’s products, particularly for businesses like SaaS companies and e-commerce platforms, where technical assistance often plays a key role in customer satisfaction.
Core Responsibilities of Customer Support Teams
- Handling technical inquiries: Customer support agents assist customers with troubleshooting, resolving bugs, and other technical problems.
- Offering technical expertise: Support professionals provide detailed guidance on using a product or service effectively.
- Providing first contact resolution: Ensuring that customer issues are resolved quickly and effectively at the first point of contact.
- Managing customer queries through various channels: Support teams address concerns via email, chat, phone, and self-service portals.
- Recording customer feedback: Insights from customer support help improve products and enhance the overall customer experience.
Key Characteristics of Customer Support
- Focuses on problem-solving for technical issues or non-technical account matters.
- Relies heavily on technical knowledge and specialized training.
- Often involves reactive assistance, responding to customer-reported issues.
- Plays a direct role in building customer confidence by resolving frustrations.
Customer support evolved from being just a reactive function to one that proactively enhances customer satisfaction by guiding users and improving products. Effective customer support is vital for customer retention and helps businesses grow by ensuring satisfied customers at every stage of the customer lifecycle.
Defining Customer Service
Customer service goes beyond resolving issues; it’s about creating a positive and lasting impression at every touchpoint of the customer journey. While it may include addressing customer inquiries, its primary focus is fostering loyalty and building relationships that contribute to business growth.
Core Responsibilities of Customer Service Teams
- Providing excellent customer service: Ensuring each interaction leaves customers feeling valued.
- Answering customer questions: Addressing inquiries related to products, policies, or services during and after the purchasing process.
- Offering personalized service: Tailoring solutions to meet individual customer needs.
- Educating customers: Helping customers understand the full value of a product or service.
- Building strong customer relationships: Proactively engaging with customers to ensure long-term loyalty.
Key Characteristics of Customer Service
- Customer service aims to ensure a seamless customer experience by focusing on satisfaction and trust.
- It’s often proactive, anticipating customer needs before they arise.
- Involves non-technical support, such as resolving complaints, processing returns, and providing information.
- Customer service agents need customer service skills, such as active listening, empathy, and strong communication.
The Role in Business Success
Customer service is the backbone of a customer-centric approach. By consistently delivering great customer service, companies can:
- Build customer loyalty.
- Drive customer retention by keeping current customers happy.
- Turn satisfied customers into advocates, boosting reputation and attracting new customers.
Effective customer service plays a crucial role in creating exceptional customer experiences. By addressing customer needs with empathy and understanding, businesses can turn even frustrated customers into loyal brand ambassadors.
Key Differences Between Customer Support and Customer Service
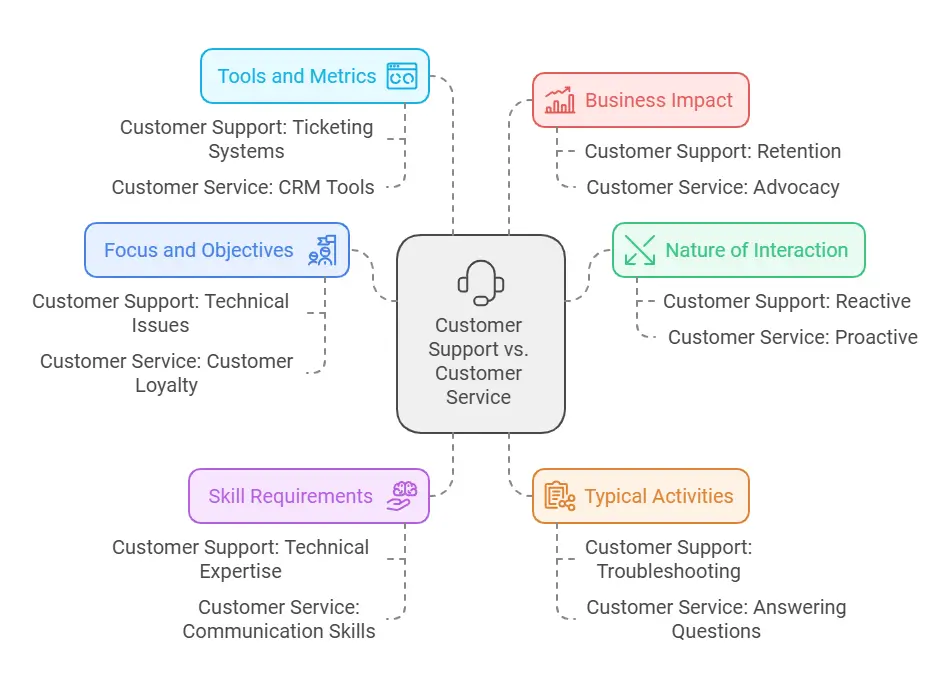
While customer support and customer service both focus on improving the customer experience, they differ in their goals, approaches, and areas of expertise. Let’s explore their distinctions to understand how they contribute to business success.
1. Focus and Objectives
- Customer Support: Primarily addresses technical issues and ensures products function as intended. The goal is to provide technical assistance and resolve problems swiftly.
- Customer Service: Encompasses broader activities like fostering loyalty, guiding customers through the purchasing process, and building strong customer relationships.
2. Nature of Interaction
- Customer Support: Usually reactive, responding to customer inquiries or problems after they arise.
- Customer Service: Often proactive, aiming to anticipate and meet customer needs to provide a seamless customer experience.
3. Skill Requirements
- Customer Support Teams: Need technical expertise to handle complex issues related to a company’s products.
- Customer Service Teams: Require customer service skills like active listening, empathy, and clear communication to deliver personalized service.
4. Typical Activities
- Customer Support:
- Troubleshooting technical problems.
- Guiding users on self-service portals.
- Assisting with non-technical account issues like login or billing problems.
- Customer Service:
- Answering customer questions about products and services.
- Providing information on policies or return processes.
- Ensuring customer satisfaction through thoughtful engagement.
5. Tools and Metrics
- Customer Support: Often relies on specialized tools like ticketing systems, knowledge bases, and product guides. Success is measured by metrics like first contact resolution and time-to-resolution.
- Customer Service: Uses tools for customer relationship management (CRM), feedback collection, and interaction tracking. Metrics include customer satisfaction scores (CSAT), net promoter scores (NPS), and retention rates.
6. Business Impact
- Customer Support Focuses: On solving issues to retain customers and prevent churn.
- Customer Service Aims: To enhance the customer journey, boost loyalty, and drive advocacy.
Why Both Are Important
Businesses that invest in both customer support and customer service create a balanced strategy. While customer support resolves immediate concerns, customer service ensures long-term satisfaction, leading to business success. Together, they build customer confidence and foster trust throughout the customer lifecycle.
Importance of Both Roles in Business Operations
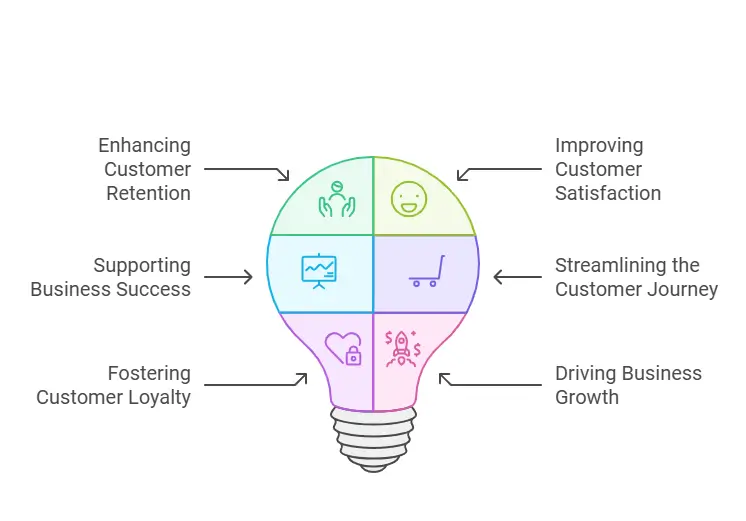
Both customer support and customer service are vital for creating a positive customer experience and driving business growth. While each role has distinct responsibilities, their combined efforts directly impact customer satisfaction and loyalty.
1. Enhancing Customer Retention
- Customers who receive good customer support for technical issues and great customer service for general inquiries are more likely to remain loyal.
- Both roles help resolve frustrations, ensuring customers feel valued and confident in their choice.
2. Improving Customer Satisfaction
- By addressing customer needs promptly and empathetically, support and service teams play a significant role in ensuring customer satisfaction.
- Proactive communication from customer service agents and efficient resolutions from customer support teams lead to more satisfied customers.
3. Supporting Business Success
- Happy customers drive referrals and advocacy, contributing to a business’s reputation and revenue.
- A seamless experience across customer-facing teams can differentiate a business from competitors, attracting new customers and retaining existing ones.
4. Streamlining the Customer Journey
- Customer support focuses on resolving technical obstacles, helping customers use products effectively.
- Customer service encompasses a broader approach, offering guidance and maintaining engagement throughout the customer lifecycle. Together, they ensure a smooth and enjoyable experience at every stage of interaction.
5. Fostering Customer Loyalty
- Businesses that invest in both customer service and support foster stronger relationships. Personalized support, quick resolutions, and thoughtful interactions encourage repeat business and long-term loyalty.
6. Driving Business Growth
- Exceptional support and service encourage customers to share positive feedback, whether through reviews or social media, boosting the brand’s visibility.
- Businesses that excel in these areas often see increased retention rates, higher satisfaction scores, and stronger revenue growth.
Integrating Customer Support and Customer Service
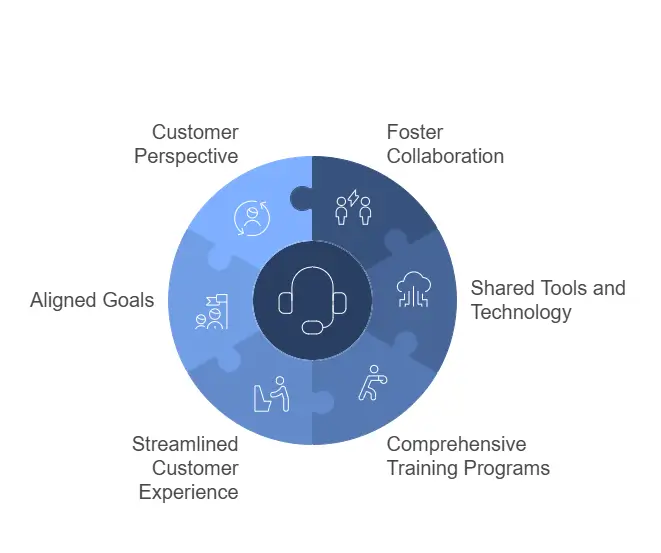
Aligning customer support and customer service teams is essential for creating a seamless and unified approach to customer interactions. While each function has unique goals, their integration ensures consistent and exceptional experiences across the customer journey.
1. Foster Collaboration Between Teams
- Encourage regular communication between customer support agents and customer service representatives.
- Share insights from both teams, such as common customer issues, feedback, and improvement opportunities.
- Use collaborative platforms or joint meetings to align on goals and strategies.
2. Adopt Shared Tools and Technology
- Implement systems like customer relationship management (CRM) software to centralize data.
- Use self-service portals and knowledge bases that support both technical and non-technical customer needs.
- Leverage analytics tools to track performance metrics for both roles, such as contact resolution rates and customer satisfaction scores.
3. Develop Comprehensive Training Programs
- Equip teams with customer service skills, such as empathy and active listening, alongside technical expertise for resolving complex issues.
- Conduct cross-training to ensure customer service agents understand support processes and vice versa.
- Emphasize the importance of teamwork in fostering customer loyalty and improving customer retention.
4. Streamline the Customer Experience
- Define clear escalation pathways, ensuring technical issues or complaints are addressed by the appropriate team without delays.
- Maintain consistent messaging across all interactions to provide high-quality service.
- Offer multi-channel support (social media, phone, chat) to assist customers in their preferred way.
5. Align Goals to Drive Business Success
- Set shared objectives for both teams, such as enhancing customer satisfaction or reducing customer frustration.
- Use unified performance metrics to measure success and identify areas for improvement.
- Highlight how both teams contribute to the company’s overall business growth.
6. Prioritize the Customer’s Perspective
- Focus on delivering a seamless customer experience by anticipating customer needs.
- Use customer feedback to refine processes and improve service.
- Ensure all interactions leave a positive impression, fostering satisfied customers who are likely to advocate for the brand.
Industry-Specific Perspectives on Customer Support and Customer Service
The roles of customer support and customer service vary across industries. While the core principles remain the same, their implementation adapts to industry-specific needs and customer expectations. Let’s explore how these functions differ for SaaS companies, e-commerce businesses, SMEs, and SMBs.
1. SaaS Companies
- Customer Support Focus:
- Handles technical issues like software bugs, login problems, or feature troubleshooting.
- Guides users on optimizing tools and features to maximize value.
- Customer Service Focus:
- Educates customers on product capabilities during onboarding.
- Helps with non-technical inquiries like billing and subscription management.
- Unique Challenges: SaaS companies must balance proactive education with responsive support to maintain customer confidence and prevent churn.
2. E-Commerce Businesses
- Customer Support Focus:
- Addresses technical problems with website navigation, payment gateways, or order tracking.
- Resolves product defects or return issues.
- Customer Service Focus:
- Handles customer questions about products, shipping policies, and promotions.
- Enhances the purchasing process by offering tailored recommendations.
- Unique Challenges: Delivering great customer service at scale during peak shopping seasons, while ensuring quick contact resolution.
3. SMEs (Small and Medium Enterprises)
- Customer Support Focus:
- Resolves technical queries related to software or tools used in operations.
- Provides assistance to ensure smooth usage of products and services.
- Customer Service Focus:
- Manages inquiries about policies, pricing, or partnerships.
- Builds strong customer relationships through personalized support.
- Unique Challenges: Limited resources may require teams to handle both technical and non-technical concerns efficiently.
4. SMBs (Small and Medium Businesses)
- Customer Support Focus:
- Solves customer issues related to software integration or product usage.
- Maintains a proactive approach to reducing customer frustration.
- Customer Service Focus:
- Guides customers through purchasing and post-purchase support.
- Uses feedback to improve service offerings.
- Unique Challenges: Balancing cost-effective solutions with the need for high-quality service
Best Practices and Tools for Customer Support and Customer Service
Combining the right strategies with effective tools ensures that both customer support teams and customer service teams operate efficiently. Here are best practices and tools to optimize their performance and enhance customer satisfaction.
Best Practices
- Provide Ongoing Training
- Train customer support agents on technical problem-solving and product knowledge.
- Equip customer service representatives with soft skills like active listening, empathy, and conflict resolution.
- Conduct cross-training to ensure teams can handle overlapping responsibilities seamlessly.
- Leverage Self-Service Options
- Offer knowledge bases, FAQs, and self-service portals to empower customers to resolve issues independently.
- Reduce the workload on support teams while improving the customer experience.
- Focus on First Contact Resolution
- Prioritize resolving customer issues in the first interaction to minimize frustration and build trust.
- Use tools like ticketing systems to track and streamline issue resolution.
- Personalize Customer Interactions
- Tailor solutions and recommendations based on customer history and preferences.
- Use data from customer relationship management (CRM) systems to personalize support.
- Collect and Act on Customer Feedback
- Regularly gather feedback to identify improvement areas.
- Use insights to enhance both technical support and overall service quality.
- Integrate Across Teams
- Foster collaboration between customer support professionals and customer service agents.
- Share knowledge and metrics to maintain a consistent approach to customer interactions.
Essential Tools
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software
- Centralizes customer data for customer-facing teams to access and use effectively.
- Examples: Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM.
- Help Desk and Ticketing Systems
- Helps support teams manage and resolve issues efficiently.
- Examples: Zendesk, Freshdesk, Jira Service Management.
- Live Chat and Messaging Platforms
- Facilitates real-time communication for addressing customer questions quickly.
- Examples: Intercom, Drift, LiveChat.
- Knowledge Base Tools
- Creates a repository of guides, FAQs, and tutorials for customers to use.
- Examples: Document360, Helpjuice, Confluence.
- Feedback Collection Tools
- Enables teams to gather customer feedback on service quality and satisfaction.
- Examples: SurveyMonkey, Typeform, Qualtrics.
- Performance Analytics Tools
- Tracks key metrics like contact resolution, response times, and customer satisfaction scores (CSAT).
- Examples: Tableau, Google Analytics, Power BI.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between customer support and customer service is key to providing a well-rounded and satisfying customer experience. While customer support focuses on resolving technical issues and ensuring smooth product usage, customer service takes a broader approach by building relationships and fostering loyalty.
Together, these roles create a powerful synergy. By aligning support teams and customer service teams, businesses can:
- Enhance customer satisfaction.
- Build strong customer relationships.
- Boost customer retention.
Investing in effective strategies and the right tools for both customer support and customer service ensures that every interaction contributes to long-term business success. Whether you’re a SaaS company, an SME, or an e-commerce business, prioritizing these functions will help you stay competitive and grow your brand.
FAQs
1. What is the key difference between customer support and customer service?
Customer support handles technical problems and focuses on ensuring that products work as intended. Customer service addresses broader needs, focusing on relationship building and guiding customers through the customer journey.
2. Why are both customer support and customer service important?
These functions address different aspects of customer interactions. While customer support ensures products work smoothly, customer service fosters loyalty and enhances the overall experience. Both are essential for retaining satisfied customers and driving business growth.
3. What skills are critical for customer support agents?
Customer support agents need technical expertise, problem-solving abilities, and clear communication skills to resolve customer issues effectively.
4. What skills are critical for customer service representatives?
Customer service representatives require strong interpersonal skills like empathy, active listening, and conflict resolution to ensure excellent customer service.
5. How do tools like CRMs help customer-facing teams?
CRMs centralize customer data, enabling teams to provide personalized service and track key metrics like customer satisfaction scores (CSAT).