Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF) might ring a bell. You might know it from phone keypads. But its role in telecommunication systems is more complex. To understand DTMF, you must know how it turns tones into useful data.
Its uses range from improving interactive voice response systems to making banking transactions safe. DTMF's wide use makes it crucial in today's communication technology. It helps smooth data transmission. This raises interesting thoughts about its future improvements and changing roles in telecommunications.
I. Understanding Dual-tone Multi-frequency
Grasping Dual-tone Multi-frequency means breaking down two simultaneous tones into matching digits for phone communication.
DTMF technology uses signals to reflect numbers, letters, and symbols on a phone keypad. Pressing keys creates a unique mix of frequencies, helping data send easily over phone lines.
This technology is key in many voice response systems and phone services.
II. Application and Benefits of DTMF
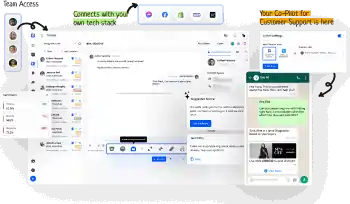
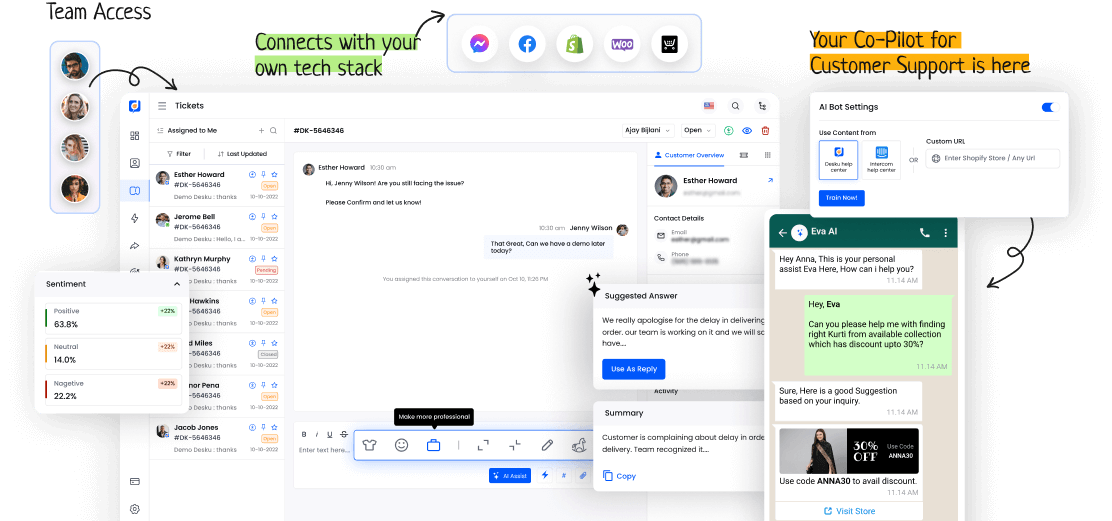
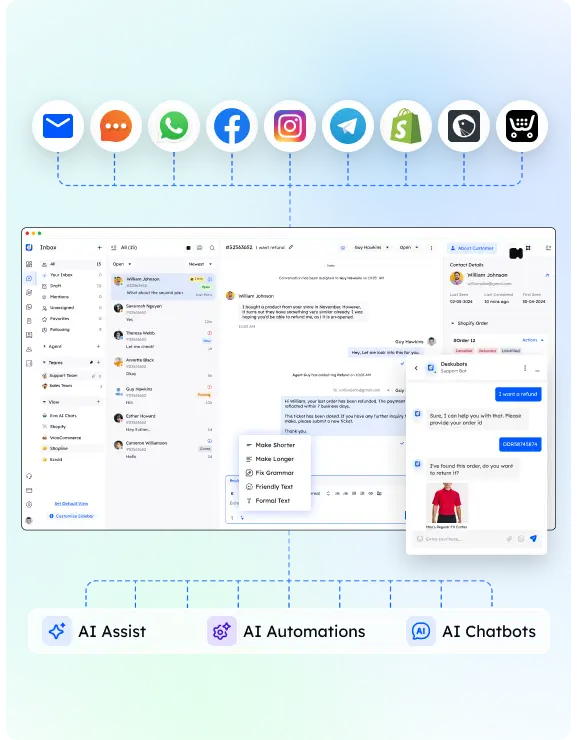
DTMF technology is vital in today's telecom systems. It has many uses and benefits. It works in phone menu systems and remote equipment control.
Its perks include quick call routing, better user experience, and efficient automated services. DTMF simplifies communication and ensures smooth interactions. It's a valuable tool in many industries.
III. DTMF in Telecommunication Systems
In telecom systems, Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF) tech is key. It makes communication smooth. DTMF is used in many telecom rules. It turns signals into tasks like dialing numbers or talking to automated systems. Here is a table showing DTMF use in telecom systems:
| Telecom Rules | Signal Turning |
|---|---|
| VoIP | DTMF sounds |
| Landline Phones | Touch-Tone |
| Mobile Networks | Keypad use |